5G Technology :Is speed Bringing Risk too
5G Technology :Is speed Bringing Risk too
In today’s fast paced digital world, technology is evolving rapidly, transforming the way we live, work, and communicate. Among the most revolutionary advancements is 5G technology the fifth generation of wireless communication. It promise ultra fast internet, low latency, and a hyper connected world. however, with great speed comes great responsibility. As 5G rolls out globally, questions safe? does it carry hidden threats alongside its numerous benefits?
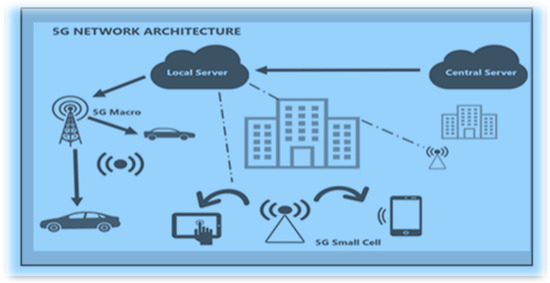
What is 5G technology
5G stands for fifth generation mobile network technology. It follows 1G to 4G and represents a major leap in wireless communication. while 4G offers maximum speeds up to 100 mbps,
5G can theoretically deliver speeds up to 10 Gbps.
Moreover it drastically reduces latency to just 1 millisecond, enabling near real time communication. this level of speed and responsiveness has unlocked possibilities in several domains, including remote surgeries, autonomous vehicles, other vehicles.

Security Risk and Cyber Vulnerabilities
However, the advantages of 5G come with significant risks. perhaps the most pressing are cybersecurity threats. as 5G network enable more connected devices and critical infrastructure they also expand the attack surface for malicious actors.
Unlike previous generations, 5G relies heavily on software defined networking and virtualization making it more complex and potentially more vulnerable Hacker could exploit these new digital pathways to infiltrate system, steal data or disrupt services. A cyberattack on a 5G powered smart grid or healthcare system could have catastrophic consequence endangering live and national security.
Moreover, with the proliferation of IoT device ranging from smart thermostats to industrial machine the chance of weak links in the network grow. many of these devices are not built with security as a primary concern making them easy targets for cybercriminals. once compromised these device can serve as entry points into large network.
Privacy Concerns and Data Exploitation
5G’s capability to handle more data also raise significant privacy concerns. As people, vehicle, and even appliances become continuously connected the amount of personal data generate will skyrocket this data can include location behavioral pattern, health information, and even biometric details.
Telecom companies, tech firm, and advertisers could potentially exploit this data to target consumers more aggressively. Government, too, may use enhanced surveillance tools enabled by 5G to monitor citizens. while this might be justified for security purposes, it also raises questions about civil liberties and the right to privacy.
The increased surveillance potential has sparked debates in democratic societies about how much oversight is appropriate and what safeguards need to be implemented. without strong data protection laws and transparent practices, the power of 5G could easily be misused.
What is 5G low latency?
A millisecond is 1/1000 of a second.
The average reaction time for humans to a visual stimulus is 250 ms or 1/4 of a second. People are capped at around 190-200 ms with proper training.
Imagine now that your car could react 250 times faster than you.
Imagine it could also respond to hundreds of incoming information and communicate its reactions to other vehicles and road signals within milliseconds.
At 60 mph (100km/h), the reaction distance is about 33 yards (30 meters) before you pull on the brakes. With a 1ms reaction time, the car would only have rolled more than one inch (less than 3 centimeters).
Use cases associated with low latency are:
- V2X (Vehicle to Everything) communication: V2V: (Vehicle-to-Vehicle), V2I (Vehicle-to-Infrastructure), autonomous, connected car
- Immersive Virtual Reality Gaming (5Gwill bring VR to the masses.)
- Remote surgical operations (aka telesurgery)
- Simultaneous translating
5G and the previous mobile generations at a glance
In the last four decades, mobile phones, more than any other technology, have quietly changed our lives forever.
- 1G, the first generation of telecom networks (1979), let us talk to each other and be mobile
- 2G digital networks (1991) let us send messages and travel (with roaming services)
- 3G (1998) brought a better mobile internet experience (with limited success)
- 3.5G brought a truly mobile internet experience, unleashing the mobile app ecosystem
- 4G (2008) networks brought all-IP services (Voice and Data), a fast broadband internet experience, with unified network architectures and protocols
- 4G LTE (for Long Term Evolution), starting in 2009, doubled data speeds. While LTE boasts extensive network coverage, 5G is still in the initial phases of being rolled out.
- 5G networks (2019) expand broadband wireless services beyond mobile internet to IoT and critical communications segments.
Virtual networks (5G slicing) tailored to each use case.
5G will support all communication needs from low-power Local Area Networks (LAN) – like home networks, such as Wide Area Networks (WAN), with the proper latency/speed settings.
This need is addressed today by aggregating various communication networks (Wi-Fi, Z-Wave, LoRa, 3G, 4G, etc.)
And 5G is more innovative.
5G is designed to allow simple virtual network configurations to align network costs with application needs better.
This new approach will allow 5G Mobile network operator to catch a larger IoT market by delivering cost-effective solutions for low-band, low-power applications.
Some recent illustrations:
- Hewlett-Packard builds a private network for the 2023 Ryder cup (September 2023).
- NTT and Las Vegas launch the largest private 5G network in the US (September 2022)
- Porsche and Vodafone build a hybrid private network (December 2022).
What is 5G+?
5G+ is a step up from standard 5G, designed to boost network speed, capacity, and coverage by as much as 50%.
Imagine at busy events, like concerts or games, 5G+ cuts through digital crowd jams, letting you download an HD movie in a minute.
While standard 5G utilizes low-band spectrum to extend coverage and enhance reliability, it delivers speeds only marginally faster than 4G LTE.
On the other hand, 5G plus leverages millimeter wave technology to achieve breakneck speeds, though with a shorter range.
What are the real 5G use cases?
Each new generation wireless network came with a new set of new usages.
The next 5G will make no exception and focus on IoT and critical communications applications.
In terms of the schedule, we can mention the following use cases over time:
- Fixed wireless access (from 2018-2019 onwards)
- Enhanced mobile broadband with 4G fallback (from 2019-2020-2021)
- Massive M2M / IoT (from 2021-2022)
- Ultra low-latency IoT critical communications (from 2024-2025)

When is 5G coming?
5G rollout: Where do we stand?
Over four years since its launch, 5G technology has significantly matured, achieving broader and faster coverage.
Mid 2024, 5G has reached 1.7 billion subscriptions globally, with an addition of 160 million in the first quarter alone. About 320 service providers have established 5G networks, and 49 have launched 5G Standalone (SA) networks. User have over 2,300 5G devices models to choose from.
By 2029, 5G is expected to encompass 5.6 billion subscriptions, overtaking 60% of all mobile subscriptions.
5G speed in 2023-
Speed-wise, 5G is transforming digital experiences with average download speeds many times faster than 4G, with India (19.2x), Malaysia (14.4x), and Brazil (13.5x) witnessing the most significant jumps.
Regarding absolute speeds, South Korea leads at 432.5Mbps, with seven markets exceeding 300 Mbps. For gaming and video streaming, 5G provides an enhanced experience, with improvements of up to 37.6% in video and 31.3% in gaming experiences across various markets.
5G availability
Regarding availability, South Korea and Puerto Rico are leading, with nearly half of their 5G users spending most of their time connected to 5G, according to Opensignal benchmarks of June 2023.
The US follows closely with a 31.1% availability rate. However, availability varies in Europe, with Finland and Bulgaria at the top (24.2% – 24.7%) but significant markets like the UK lagging behind (10.1%).
Singapore and Taiwan are at 30% in Asia, with Malaysia at 20.5%.